Summary of Oil Field Operations
Associated gas is natural gas produced with crude oil from the same reservoir, which can be dissolved in the oil at reservoir conditions or form a cap of "free gas" above the oil. Appraisal wells are wells drilled as part of an appraisal drilling program to determine the size, reserve, and estimated production rate of an oil field.
Antifoam is a chemical additive used to lower interfacial tension to prevent trapped gas from forming a foam. Treatment fluid is designed to resolve a specific wellbore or reservoir condition, used for stimulation, isolation, or control of reservoir gas or water. Slurry is a mixture of suspended solids and liquids. Alkaline flooding is an oil recovery technique where an alkaline chemical reacts with the oil, forming surfactants inside the reservoir. Water is injected into the reservoir to displace residual oil, moving the displaced oil to adjacent production wells.
Abrasive jetting is a wellbore treatment using a fluid containing solid particles to remove deposits from the surface of the wellbore and/or completion components. Barrel of Oil EQ (BOE) is a unit of energy used to measure the volume of petroleum and related products. BBL refers to a barrel of oil, BCF refers to a billion cubic feet of natural gas, BCM means a 'billion cubic meters' and is generally used to measure natural gas. Bit is a drilling tool used to cut a cylindrical hole in the earth's crust, while block is a geographical area of land where an oil or gas reservoir lies.
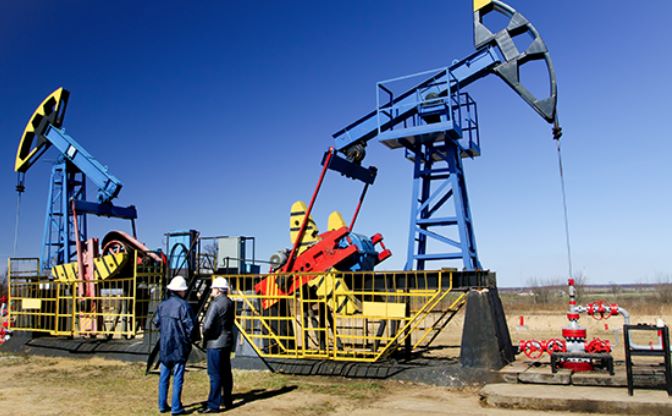
Contingent resources are quantities of petroleum estimated to be recoverable from known accumulations. Conventional oil is oil found or expected to be found within a conventional reservoir. Core and coring is a process associated with drilling to assess the productivity of oil well drilling. The creaming curve is a statistical technique used to present the relationship between aggregated or cumulative resource from wells drilled. Derrick is a tower-like structure housing drilling controls and lifting equipment. Development wells are drilled in proven areas of an oil or gas reservoir to maximize economic production and recovery of reservoirs known reserves.
Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR) is a process that uses advanced techniques to increase oil recovery from oil reservoirs. It involves three major recovery types: chemical flooding, miscible displacement, and thermal recovery. Exploration wells are concentrated areas for drilling to determine hydrocarbon presence, while erosion corrosion is a common cause of failure in oilfield equipment. Fields, which contain large amounts of oil or gas, produce millions of barrels of oil daily.
Retrieval involves understanding the dimensions and nature of the "fish" in a wellbore, wellbore conditions, tools, and the process of handling the recovered fish. Fracture/fracking is a method of breaking down a rock formation to force open existing fissures. Gas fields contain natural gas, and gas injection maintains reservoir pressure with separate gas pumped back into the reservoir for conservation.
Gas in Place (GIP) or Gas Initially in Place (GIIP) is the quantity of estimated gas in naturally occurring accumulations before extraction or production. Gas Lift is the process of raising or lifting fluid from a well by injecting gas through tubing into the well. The Gas Oil Ratio (GOR) refers to the number of cubic feet of gas produced per barrel of oil.
Improved Oil Recovery (IOR) involves processes that improve the flow of hydrocarbons from a reservoir to the wellbore, such as Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR). Infill Wells are wells drilled into existing reservoirs between wells already producing oil/natural gas, while Injection Wells inject water or gases into the reservoir to maintain pressure. In-situ Recovery techniques extract hydrocarbons from beneath the surface without removing soil and other materials.